Let's start with the main question, what is a Chemical Bond?
Simply explained, Chemical Bonding refers to the formation of a chemical bond between two or more atoms, molecules, or ions to give rise to a chemical compound. These chemical bonds are what keep the atoms together in the resulting compound.
"We had to have the ideas about partial ionic character of covalent bonds, you know, which I developed in about ’33, ’32, before it became possible to discuss electro-neutrality in a very significant way."
- Linus Pauling.

The Basics of Bonding
Chemical bonds are formed when electrons in different atoms interact with each other to make an arrangement that is more stable than when the atoms are apart.
What causes atoms to make a chemical bond with other atoms, rather than remaining as individual atoms? For this, we need to consider the noble gas elements, (the column furthest right on the periodic table).
These elements helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon, do not form compounds very easily, which suggests that they are especially stable as lone atoms.
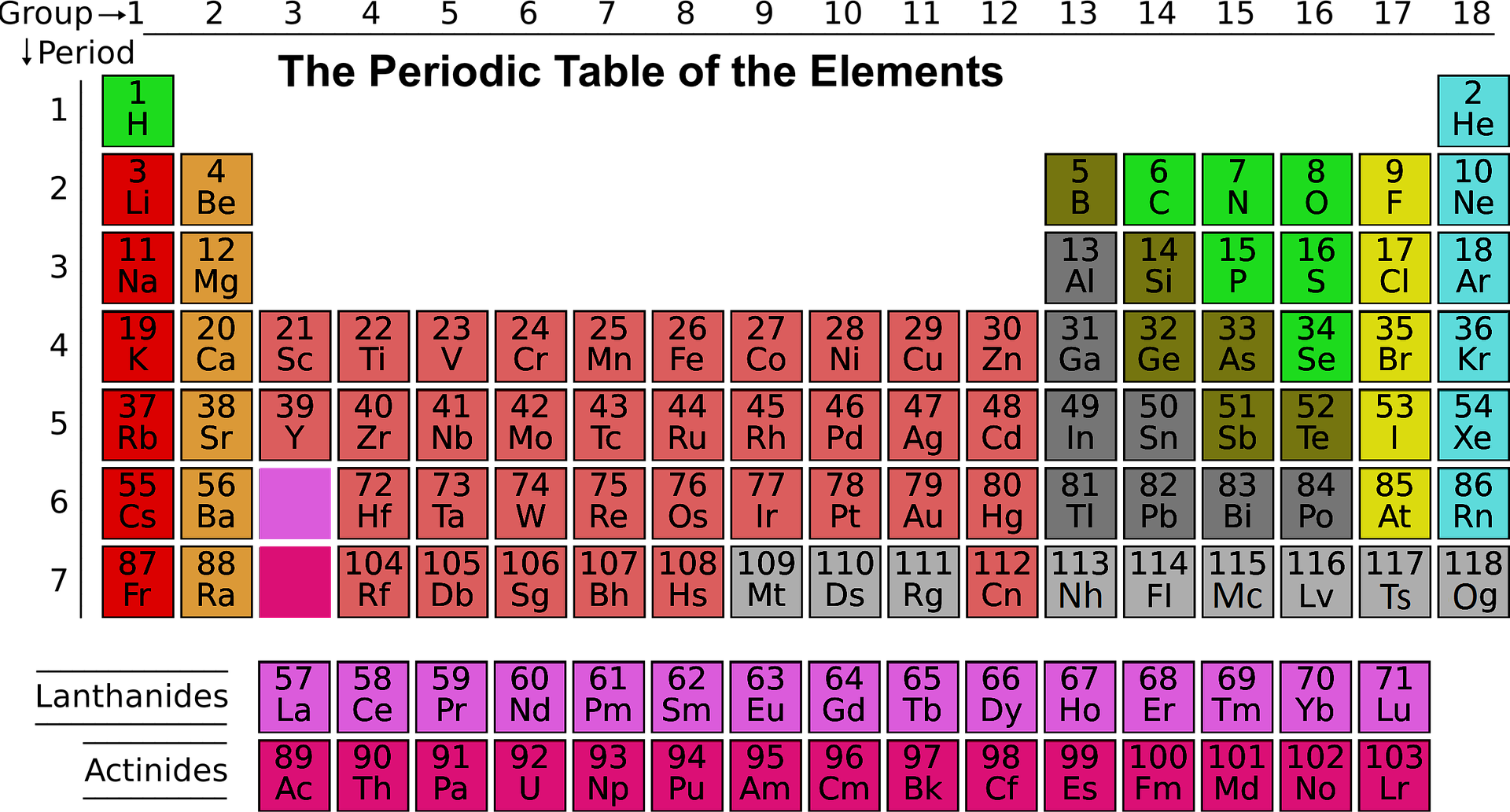
The periodic table is a chart that arranges chemical elements in a useful, logical manner. Elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number, lined up so elements that exhibit similar properties are arranged in the same row or column as others.
What else do the noble gas elements have in common?
Except for helium, they all have eight valence electrons. Chemists have concluded that atoms are especially stable if they have eight electrons in their outermost shell. This useful rule of thumb is called the octet rule, and it is a key to understanding why compounds form.
When two atoms approach each other, these outer electrons start to interact. Although electrons repel each other, they are attracted to the protons within atoms. The interplay of forces results in the formation of bonds between the atoms.
A bond between two atoms depends upon the electronegativity difference between the atoms. If the electronegativity difference is significantly high, the atoms transfer electrons to form ions and thereby form an ionic bond. If the electronegativity difference is zero or small, then the atoms combine to form covalent bonds.
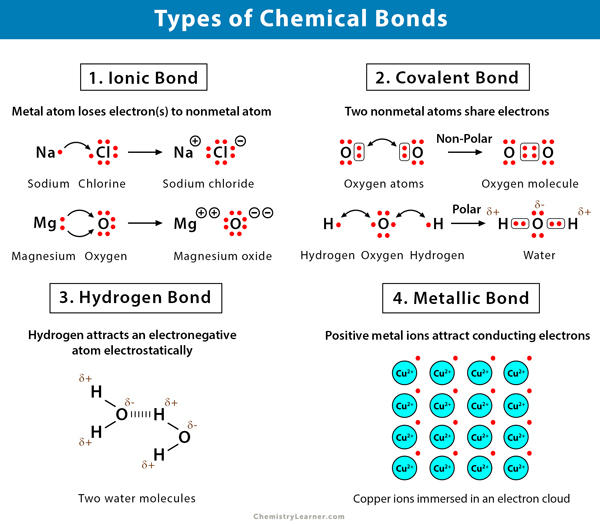
4 Main Types of Chemical Bonding
There are three primary types of bonding:
- Ionic bonding.
- Covalent bonding.
- Hydrogen bonding.
- Metallic bonding.
Ionic Bond
As the name suggests, ionic bonds are a result of the attraction between ions. Ions are formed when an atom loses or gains an electron. The production of two oppositely charged ions, positively charged ions-cations and negatively charged ions-anions, results from this sort of bonding.
Examples:
- Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) combine to form stable crystals of sodium chloride (NaCl), also known as common salt.
- Magnesium (Mg) and oxygen (O) combine to form magnesium oxide (MgO).
- Potassium (K) and chlorine (Cl) combine to form potassium chloride (KCl).
- Calcium (Ca) and fluorine (F) combine to form calcium fluoride (CaF2).
Properties of Ionic Bonds
The following characteristics are found in ionic-bonded molecules due to the existence of a strong force of attraction between cations and anions:
- An ionic bond is the most powerful of all bonds
- The ionic bond is the most reactive of all existing bonds in an appropriate medium since it possesses charge separation
- The melting and boiling points of ionic bond compounds are pretty high
- Ionic-bonded molecules are strong conductors of electricity in their aqueous solutions or molten form. This is because ions, which function as charge carriers, are present
Covalent Bond
In the case of a covalent bond, an atom shares one or more pairs of electrons with another atom and forms a bond.
A covalent bond is formed when the electron pairs between atoms or constituents are shared. These electron pairs are said to be shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms or any constituents when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding.
Examples
- Two atoms of iodine (I) combine to form iodine (I2) gas.
- One atom of carbon (C) combines with two atoms of oxygen (O) to form a double covalent bond in carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Two atoms of hydrogen (H) combine with one atom of oxygen (O) to form a polar molecule of water (H2O).
- Boron (B) and three hydrogens (H) combine to form the polar borane (BH3).
Covalent Bond Properties
The following are some of the characteristics of covalent bonds:
- The production of additional electrons is not a result of the formation of covalent bonds.
- The bond solely links them
- There are powerful chemical bonds between atoms
- A covalent bond holds roughly 80 kcal/mol of energy.
- The atoms that are bonded have definite orientations relative to one another. Therefore covalent bonds are directional
- Covalent bonds rarely break on their own after they have been formed
- The MPs and BPs of most covalently bound substances are relatively low
- The enthalpies of vaporization and fusion are frequently lower in compounds containing covalent bonds.
- Because of the absence of free electrons in covalently bonded compounds, they do not conduct electricity.
- Water does not dissolve covalent compounds
A hydrogen bond can be defined as the attractive force that binds one molecule’s hydrogen atom with the electronegative atoms like fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen of another molecule.
Hydrogen Bond
A hydrogen bond is a chemical bond between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom. A hydrogen bond can be defined as the attractive force that binds one molecule’s hydrogen atom with the electronegative atoms like fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen of another molecule.
The magnitude of hydrogen bonding depends on the physical state of the compound, which is maximum in a solid state and minimum in a gaseous state. This allows the hydrogen bond to influence the structure and properties of the compounds strongly.
Examples
- Hydrogen atom from one molecule of water bonds with the oxygen atom from another molecule. This bonding is quite significant in ice.
- In chloroform (CH3Cl) and ammonia (NH3), hydrogen bonding occurs between the hydrogen of one molecule and carbon/nitrogen of another.
Nitrogen bases present in DNA are held together by a hydrogen bond.
Did you know to gauge whether something is an acid or base, and how strong it is, chemists, employ the pH scale?
Metallic Bond
Metallic bonding is a sort of chemical bonding that is responsible for various features of metals, including their lustrous lustre, malleability, and heat and electricity conductivities. A metallic bond is a force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. Such a solid consists of tightly packed atoms, where the outermost electron shell of each metal atom overlaps with a large number of neighbouring atoms.
Examples
- Sodium metal
- Aluminium foil
- Copper wire
Factors influencing the strength of a metallic bond:
- The total number of delocalized electrons
- The magnitude of the metal cation’s positive charge
- The cation’s ionic radius
Summarise with AI:















