It's easy to think of the world and its borders as static after a while, but it's crucial to remember that almost every historical event has the power to transform the world in significant ways.
Here are some of the most significant historical events that significantly changed the world and the course of history.

The American Revolution (1765-1783)
Throughout history, one kind of event has always affected people significantly: war. The American Revolution and the American Revolutionary War are fine examples of this.
In the 18th century, England was heavily dependent on the success of the East Indian Tea Company. When this company started to struggle, the British parliament decided to levy taxes on the American colonies.
These taxes famously included duties on tea, but the American people were more or less OK with this. Instead, it was the idea of taxation without representation. There were no representatives of the American colonies in the British parliament.
The American colonists believed no taxes should be levied against them until this was rectified. The British government, however, disagreed. The British government thought that the American colonies belonged to Britain, that those who lived there were British subjects, and that they were, therefore, represented.
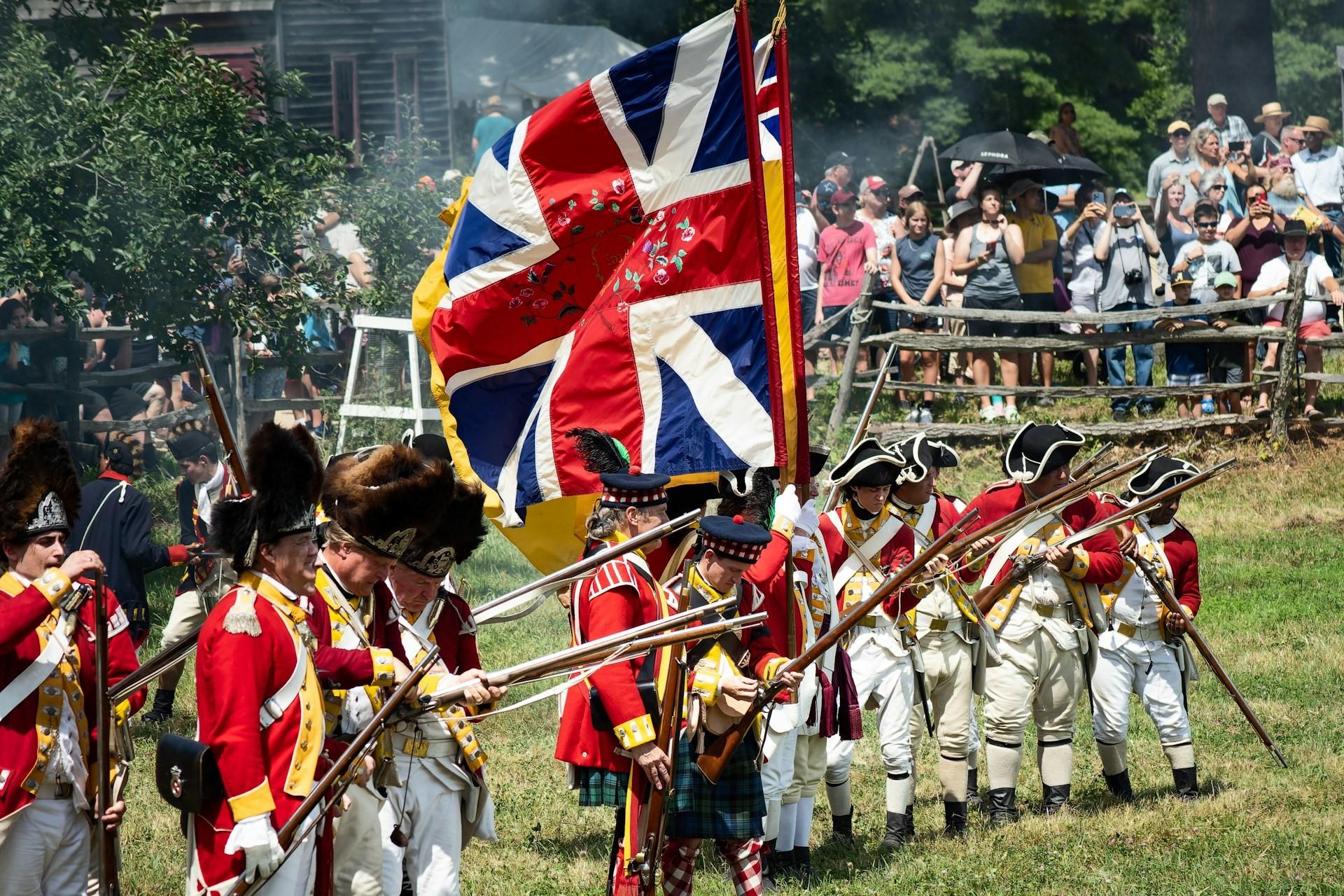

The Crown and the British government attempted to hold onto the colonies through several laws and various military acts. However, the American colonists, fueled by their belief in freedom and justice, fought against heavy taxation, unfair laws, and Britain's involvement with unwavering resilience.
The British military and American colonists regularly clashed, culminating in the American Revolutionary War or what Americans call the War of Independence.
As you can imagine, the war ultimately ended in victory for the American colonists. These historical events, including the American Revolution, have shaped global politics for the last three centuries, connecting us to a larger historical narrative.
After all, the United States of America as a sovereign nation wouldn't exist had the result of the American Revolutionary War ended in a British victory.
World War I (1914-1918)
The Great War, First World War, or World War I is often famously said to have started with the assassination of the Archduke of Austria, Franz Ferdinand.
Almost as famously, this event was preceded by a failed assassination attempt on Archduke with a grenade.
The Serb, Gavrilo Princip, who would eventually assassinate Franz Ferdinand, could only complete the assassination because of fortunate circumstances. Following a failed attempt with the grenade, Franz Ferdinand's car and motorcade intended to visit those injured in the attack.
A new route for the motorcade had been chosen, but the driver was unaware of the change. Gavrilo Princip was in a café on Franz Joseph Street on the original route and saw the car pull into the street.
The driver was informed of his mistake and attempted to turn the car around. Princip saw this opportunity and shot the Archduke. He was arrested before he could turn the gun on himself.
For a while, things were politically very tentative. The Austro-Hungarian Empire didn't immediately attack Serbia, despite their ally Germany insisting.
All the major political players in the area started mobilising their forces and reasserting their allegiances.
While the assassination was seen as the catalyst for the First World War, Europe was already in an unsteady state of alliances between major powers. There were power struggles and crises in the Balkans, and many nations were poised to take any power up for grabs.
Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia (28 Jul 1914). Chaos ensued, resulting in almost every nation eventually being dragged into conflict.
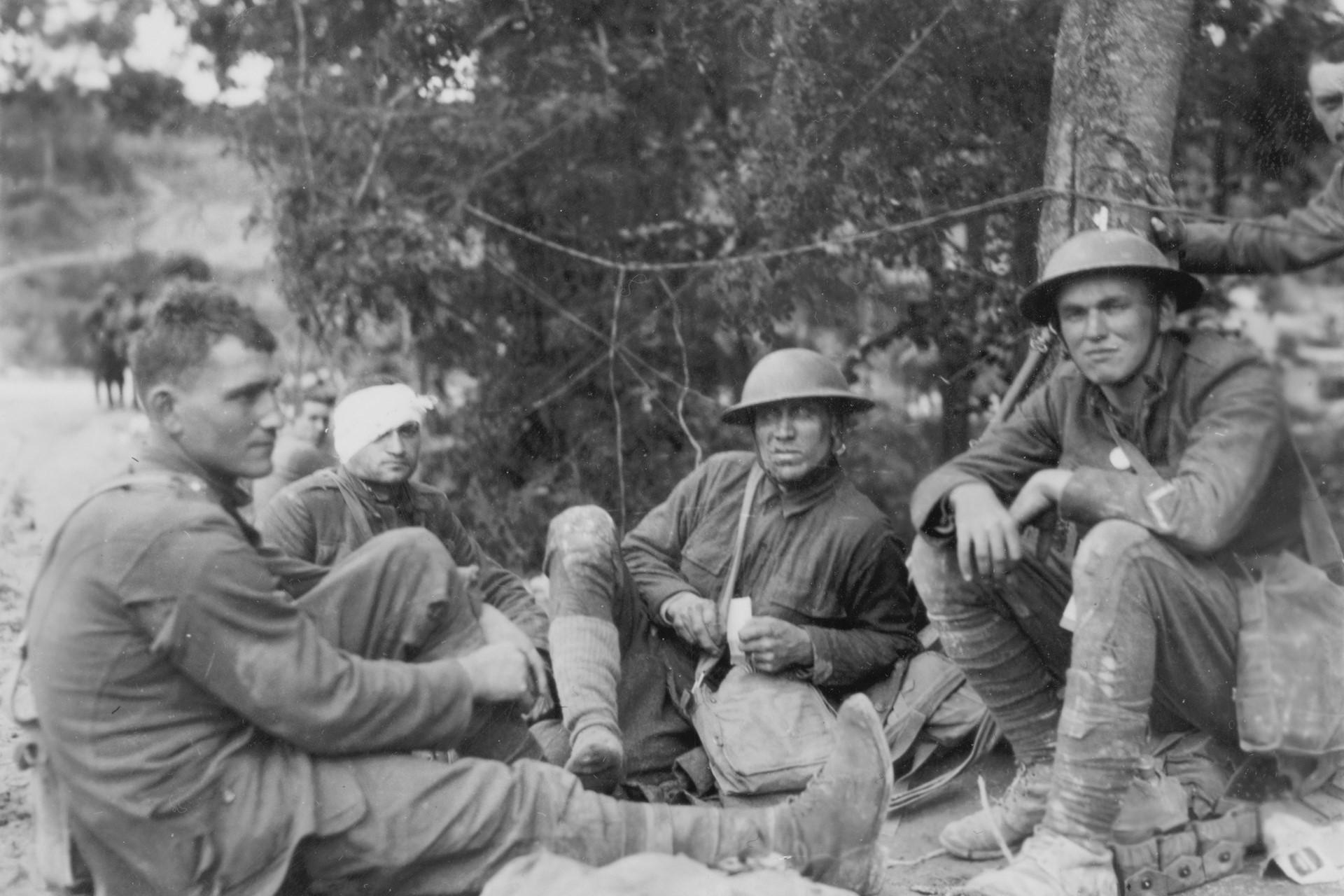

The German Empire and the Austro-Hungarian Empire were allied. Russia supported Serbia. France allied with Russia, and despite Germany's best efforts, the United Kingdom didn't remain neutral; instead, it allied with the Entente powers.
The First World War lasted four years and was fought mainly across Europe, the Middle East, parts of Africa and Asia-Pacific. With around 9 million military deaths, it was one of the deadliest in history at the time.

The Russian Revolution (1905, 1917)
The Russian Revolution can refer to either an event in 1905 or in 1917. Tsar Nicholas II of the Russian Empire was unlikely to go down in history as a great ruler. Instead, he regularly ignored important advice and misunderstood public sentiment or completely ignored it.
Peaceful protesters marched on the Winter Palace in St. Petersburg with a petition to the Tsar (On 22 Jan 1905). The Russian Imperial Guard fired upon the crowd, killing and wounding hundreds of them.
This led to strikes and unrest among the Russian peasant class. Workers went on strikes, there were military mutinies, and peasants seized land.
The workers' councils, known as Soviets, were formed in many cities across Russia.
This culminated in the October Manifest (17 Oct, 1905), with Tsar Nicholas II promising various civil liberties, a legislative parliament.
However, his promises weren't kept, and the government became repressive, regularly attempting to suppress the working class and crush dissent.
The February Revolution took place in 1917, during World War I. This was during February on the Julian calendar, though it is during March on our regular calendars.
There were clashes with the police in Petrograd (now St. Petersburg), the Duma (legislative parliament) refused to disband, and a provisional government was set up after three centuries of Romanov rule in Russia.
According to the Julian Calendar (Nov 1917; Gregorian Calendar), the October Revolution occurred in October 1917. Anger at Russia's ongoing involvement in World War I and economic hardships led to the Bolsheviks seizing key locations.

The provisional government was overthrown after less than a year in charge, the Bolsheviks took control, and a civil war broke out between the Bolsheviks (the Red Army) and the anti-Bolshevik forces (the White Army).
The Great Depression (1929-1939)
While you might think that The Great War would have led to the Great Depression but, while people were certainly affected economically by the war, the 1920s in the United States of America were notable for an economic boom, not the opposite.
War heroes returned home, women led a cultural revolution, and industry and infrastructure changed how goods were made and consumed.
Key innovations included:
- The moving assembly line from Henry Ford helped Americans own vehicles and develop their famous car culture.
- White goods like electric washing machines and refrigerators meant hygiene, health, and diets improved nationwide.
- More people than ever started owning electrical appliances like telephones and radios.
- Homeownership in America exploded with low mortgage interest rates.
This couldn't last forever, though, and eventually, the American people seemingly had everything they needed.
Sales of consumer goods slowed, banks started failing as Americans stopped borrowing money, too, and the American economic bubble burst.
When the American stock market crashed (29 Oct 1929), it was so bad that the United States of America wasn't the only country whose economy was devastated.
The Rise of Nazism in Germany
Germany was in debt following years of war but enjoyed the 1920s economically. They were called the Golden Twenties or Happy Twenties in Germany, great years for the German economy. However, this didn't last, as it all came crashing down with the stock market crash in the United States of America and the Great Depression.
There was one man, Adolf Hitler, who'd been in prison until 1924 and was pretty confident that his brand of nationalism, Pan-Germanic sentiment, and anti-semitism were exactly what German citizens wanted.
At rallies, his speeches were met with roars of approval and by 1932, the Nazi party in Germany held the most seats in the Reichstag.
From there, President Paul von Hindenburg didn't need much convincing to appoint Adolf Hitler as the chancellor of Germany. Hitler made just two adjustments to the government and found himself single-handedly running Germany.
World War II
Germany had been banned from rearming with the Treaty of Versailles. Hitler felt that the treaty's terms had quelled Germany for years, and as soon as he had control of the country, he aimed to rebuild the economy with arms manufacturing.
With a new German army capable of military action, Germany invaded Poland (1 Sep 1939). Britain and France declared war on Germany two days later.
Initially, with most of the fighting in Europe, Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941 brought the Americans fully into the conflict, and soon, every inhabited continent on the planet had some involvement in World War II.
The Soviet Union initially partnered with Germany, but once Germany invaded (22 June 1941), it became firmly part of the Allies.
While the invasion of Poland is often seen as one of the major events that started the Second World War, other events like the ongoing conflicts between China and Japan predated what many think of as the Second World War.

The Second World War ended up being one of the most atrocious in human history and led to some of the geopolitical divisions seen in Europe and worldwide, despite two major global powers (the United States of America and the Soviet Union) having been allies during the war.
Summarise with AI: